Introduction to Azure Network Watcher
Azure Network Watcher
Azure Network Watcher provides a suite of tools to monitor, diagnose, view metrics, and enable or disable logging for Azure IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service) resources. Network Watcher allows users to monitor and troubleshoot the network health of IaaS products such as virtual machines (VMs), virtual networks (VNets), application gateways, load balancers, and more.
Network Watcher is not designed for PaaS monitoring or web analytics.
Key Features of Azure Network Watcher
Network Watcher consists of three main groups of tools and capabilities:
- Monitoring
- Network Diagnostics
- Traffic
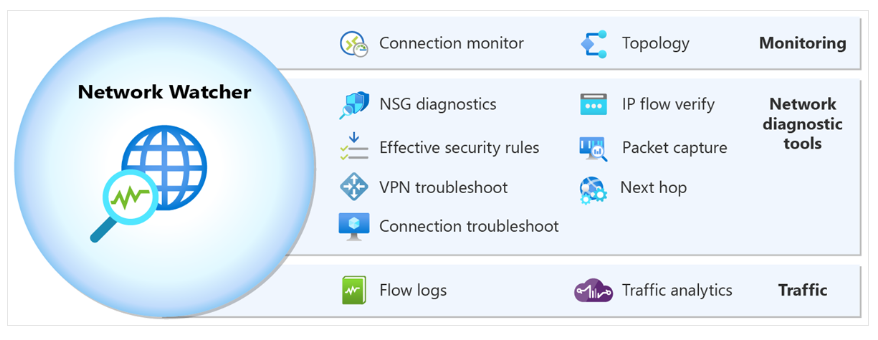
Table of Key Azure Network Watcher Features
| Category | Tool Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Monitoring | Topology | Interactive visualization of the entire network configuration, covering resources across subscriptions, resource groups, and locations. |
| Connection Monitor | Comprehensive connection monitoring between Azure and hybrid endpoints to understand network communication performance. | |
| Network Diagnostics | IP Flow Verify | Checks whether traffic is allowed or denied to/from a specific IP address and shows relevant security rules. |
| NSG Diagnostics | Diagnostics for NSG rules on VMs, VMSS, and application gateways, including adding new rules if needed. | |
| Next Hop | Determines the route of traffic and provides details on the next hop, IP address, and route table ID. | |
| Effective Security Rules | Displays the combined security rules applied to a network interface and its associated subnet. | |
| Connection Troubleshoot | Tests direct connectivity between Azure resources like VMs or URIs for instant troubleshooting. | |
| Packet Capture | Remotely captures network traffic to/from VMs or VMSS for deep analysis. | |
| VPN Troubleshoot | Diagnostics and troubleshooting of virtual network gateway connections. | |
| Traffic | Flow Logs | Records IP traffic through NSG or VNet and stores data in Azure Storage. |
| Traffic Analytics | Advanced visualization of flow logs to understand network traffic performance and patterns. |
How Azure Network Watcher Works
Azure Network Watcher is automatically enabled when a virtual network is created in an Azure region.
Users can access Network Watcher directly via the Azure portal by searching for "Network Watcher" in the search bar.
Azure Network Watcher Topology Tool
The Topology feature of Azure Network Watcher allows users to see all resources within a virtual network, including relationships between those resources. Some resource types shown include:
- Subnet
- Network Interface
- Network Security Group (NSG)
- Load Balancer
- Load Balancer Health Probe
- Public IP Address
- Virtual Network Peering
- Virtual Network Gateway
- VPN Gateway Connections
- Virtual Machine
- Virtual Machine Scale Set
Each resource in the topology has these properties:
- Name: Resource name
- Id: Resource URI
- Location: Azure region where the resource resides
- Associations: List of associations with other objects, including:
AssociationType: Relationship type (Contains or Associated)Name: Related resource nameResourceId: Related resource URI
Connection Monitor
Connection Monitor provides end-to-end connection monitoring between Azure resources and hybrid environments. Key uses include:
- Measuring latency between resources
- Detecting network or NSG configuration changes affecting connectivity
- Scheduling periodic checks on VMs to detect failures
- Providing diagnosis and remediation steps for detected issues
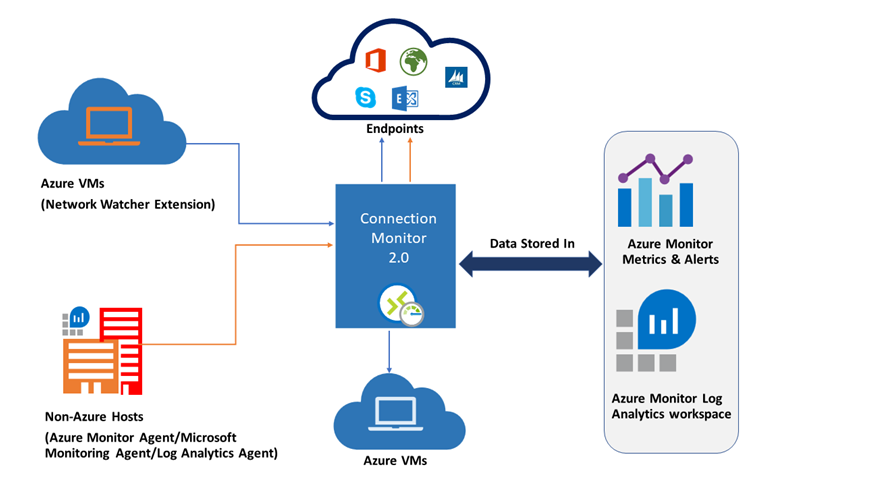
To use Connection Monitor, users need to install a monitoring agent on each monitored host:
- On Azure VMs: Use the Network Watcher Agent VM
- On on-premises servers: Use the Log Analytics Agent
IP Flow Verify
IP Flow Verify uses 5-tuple packet parameters (protocol, local port, remote port, local IP, remote IP) to verify whether traffic to/from a VM is allowed or denied. Users can specify port, protocol (TCP/UDP), local and remote IPs, as well as the VM and network adapter involved.
Next Hop
Next Hop determines the traffic route from a VM to its destination based on the effective route table of the NIC (Network Interface). This helps confirm if traffic is directed correctly.
If the route is a User Defined Route (UDR), it is displayed; otherwise, the system default route is shown.
Effective Security Rules
Effective Security Rules shows the aggregate security rules applied to a network interface. This tool helps identify why traffic is allowed or blocked by NSGs applied on VMs, subnets, or other resources.
Packet Capture
Packet Capture is a VM extension that runs remotely via Network Watcher to capture network traffic to/from a specified VM. Features include:
- Can be started via portal, PowerShell, Azure CLI, or REST API
- Supports filters based on 5-tuple
- Captured data can be saved locally on disk or to Azure Blob Storage
Connection Troubleshoot
Connection Troubleshoot tests TCP connectivity between two VMs or other endpoints. The destination endpoint can be:
- FQDN
- URI
- IP address
Successful test results include:
- Latency in milliseconds
- Number of probe packets sent
- Number of hops to the destination
If it fails, detailed error information is shown, e.g.:
- CPU: High CPU usage
- Memory: High memory usage
- GuestFirewall: Non-Azure firewall blocking the connection
- DNSResolution: Domain name cannot be resolved
- NetworkSecurityRule: NSG blocking connection
- UserDefinedRoute: Misconfigured user-defined route
VPN Troubleshoot
Network Watcher offers diagnostics for VPN connections and gateways accessible via:
- Azure Portal
- PowerShell
- Azure CLI
- REST API
VPN troubleshooting results include:
startTime: Diagnosis start timeendTime: Diagnosis end timecode: Status (e.g.,UnHealthyif there is an issue)results: Gateway or connection diagnosis resultsid: Error typesummary: Error summarydetailed: Detailed error inforecommendedActions: List of suggested actionsactionText: Explanation of actionsactionUri: Documentation linkactionUriText: Brief description of the action link
When to Use Azure Network Watcher
Azure Network Watcher is useful when troubleshooting network issues related to Azure IaaS products. Users can utilize various Network Watcher tools in these scenarios:
- Resolving connectivity problems with IaaS VMs
- Troubleshooting VPN connections
- Measuring network latency between regions
Troubleshooting IaaS VM Connectivity
Recently, a Windows Server IaaS VM was deployed to Azure, but the developer could not start a remote PowerShell session from another VM within the same virtual network.
This can be resolved using IP Flow Verify, which allows specifying:
- Local and remote ports
- Protocol (TCP/UDP)
- Local and remote IP addresses
- Connection direction (inbound or outbound)
This tool performs logical checks against NSG rules applied on the network.
Example use case:
- Enter the target VM’s IP address
- Enter TCP port 5986 (used by PowerShell over HTTPS)
- Enter the remote VM’s IP address and port
- Select TCP protocol and click Check
If an NSG rule blocks traffic, the tool will identify the specific rule responsible.
Troubleshooting VPN Connections
An IaaS VM is deployed to an Azure virtual network, with connectivity from an on-premises server via a site-to-site VPN.
Use VPN Troubleshoot in Azure Network Watcher to:
- Diagnose the virtual network gateway connection
- View VPN connection health status
This tool can be run from:
- Azure Portal
- PowerShell
- Azure CLI
It identifies common gateway issues and returns a complete diagnosis, suggesting corrective actions if the VPN connection is down.
Measuring Network Latency Between Regions
Use Network Watcher tools to measure network latency across regions, helping decide the optimal location for deploying IaaS resources.
Example:
- Deploy IaaS VMs in multiple Azure regions
- Periodically ping between VMs
- Record network latency between regions
This helps decide whether:
- All VMs should be in one region, or
- It is better to distribute VMs across regions for specific app architecture needs
If you have a hybrid on-premises and Azure IaaS app accessing the same storage endpoint, compare latencies:
- If on-premises latency is high → consider migrating to Azure
- If Azure VM latency is high → consider moving VM to a region with lower latency
When Not to Use Network Watcher
Network Watcher provides mid-level network diagnostics. It does not offer advanced features available in some third-party tools.
If your organization needs more advanced features, third-party tools may be necessary.
Important limitations:
- Network Watcher only supports IaaS resources within Azure virtual networks
- It cannot diagnose connectivity issues for PaaS services or Web Analytics
- For those, use:
- Azure Status Page
- Azure Service Health Dashboard