Protecting VMs Using Azure Backup
Azure Backup Features and Scenarios
A company's business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR) plan requires full backup and recovery capabilities for all high-risk servers. Users are required to enable and test the backup and restore functionality for these critical Windows and Linux assets.
Azure Backup vs Azure Site Recovery
Both Azure Backup and Azure Site Recovery aim to improve system resilience against disruptions and failures, but their approaches differ:
- Azure Backup focuses on retaining a consistent snapshot of data that allows rollback to a previous point in time.
- Azure Site Recovery replicates data almost in real time and enables failover operations.
Use Site Recovery for major disasters (e.g., natural disasters) and Backup for accidental data loss, data corruption, or ransomware attacks.
Choosing the right recovery approach depends on:
- The criticality of the application,
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO),
- Cost implications.
Why Use Azure Backup?
Traditional backups (like disk and tape) lack deep integration with cloud-based solutions. Azure Backup offers numerous advantages over traditional solutions:
Infrastructure-Free Backup
No need to build or manage backup infrastructure. There's no overhead in managing backup servers or adjusting storage capacity.
Long-Term Retention
Meet compliance and audit requirements by retaining backups for years. Lifecycle management automatically prunes recovery points according to policy.
Security
Azure Backup protects data in transit and at rest:
- Azure Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Grants access only to authorized users.
- Backup encryption: Backups are automatically encrypted with Microsoft-managed keys or Customer-Managed Keys (CMK) via Azure Key Vault.
- No internet connection required: Data transfers only via the Azure backbone—no public IP or FQDN needed.
- Soft delete & Enhanced soft delete: Deleted backups are retained for 14 days and can be recovered.
High Availability
Azure Backup offers three replication types:
- LRS (Locally Redundant Storage) – basic protection.
- GRS (Geo-Redundant Storage) – failover to a secondary region.
- ZRS (Zone-Redundant Storage) – synchronous replication across three Azure zones.
Centralized Monitoring and Management
Azure Backup offers built-in monitoring and alerts via the Recovery Services Vault—no extra infrastructure needed.
Supported Azure Backup Scenarios
Azure Backup supports the following scenarios:
| Scenario | Description |
|---|---|
| Azure VMs | - Backup for Windows and Linux VMs in Azure. - Backups stored in Recovery Services Vault with built-in recovery point management. |
| On-premises | - Backup files, folders, and system state using the MARS agent. - Backup on-premises VMs (Hyper-V and VMware) using MABS or DPM. |
| Azure File Shares | - Azure Backup provides snapshot management for Azure Files. |
| SQL Server and SAP HANA on Azure VMs | - Stream-based solutions for backing up SQL Server and SAP HANA. - Supports full, differential, and log backups. - Supports 15-minute RPO and point-in-time recovery. |
Azure Backup allows users to secure their data efficiently and is fully integrated with the Azure platform. It is ideal for organizations seeking a modern, cost-effective backup solution that meets global compliance standards.
Backing Up Azure VMs Using Azure Backup
Users want to ensure that the configured backup and recovery jobs provide a way to restore corporate servers. With this requirement in mind, users want to investigate the best way to apply backups for virtual machines (VMs).
VMs hosted in Azure can utilize Azure Backup. Users can easily back up and restore machines without installing additional software.
How Azure Backup Works on VMs
Azure VMs are backed up by taking disk snapshots at user-defined intervals, then transferring those snapshots to a Recovery Services Vault based on customer-defined policy.
Recovery Services Vault
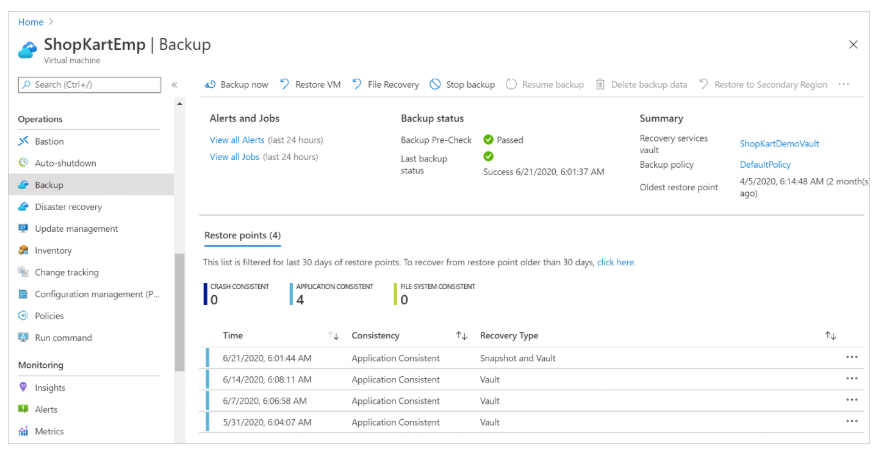
Azure Backup uses a Recovery Services Vault to manage and store backup data. The vault is a storage management entity providing a simple experience for performing and monitoring backup and restore operations.
Users do not need to manage their own storage accounts. Just specify the vault for VM backup. Backup data is automatically transferred to an Azure Backup storage account (in a separate fault domain).
The vault also acts as a role-based access control (RBAC) boundary to ensure secure access to data.
Snapshots
A snapshot is a point-in-time backup of all disks on the VM. For Azure VMs, Azure Backup uses different extensions depending on the operating system:
| Extension | OS | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VM Snapshot | Windows | Works with Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) to back up disk and memory. |
| VM SnapshotLinux | Linux | Takes a full disk copy. |
Snapshot Consistency Levels
- Application consistent: Captures memory and pending I/O. On Linux, requires custom scripts.
- File system consistent: If VSS or scripts fail, the file system remains consistent.
- Crash consistent: Occurs if the VM is powered off during backup. Does not guarantee data consistency.
Backup Policies
Users can define backup frequency and retention duration. Backups can be scheduled daily or weekly and retained for years. Azure Backup supports two data access tiers:
- Snapshot tier: Local snapshots retained for up to 5 days for fast recovery (instant restore).
- Vault tier: Snapshots copied to the vault for security and long-term retention.
With Enhanced Policy, users can enable hourly backups and perform Selective Disk Backup—backing up only critical disks from a VM.
Azure VM Backup Process
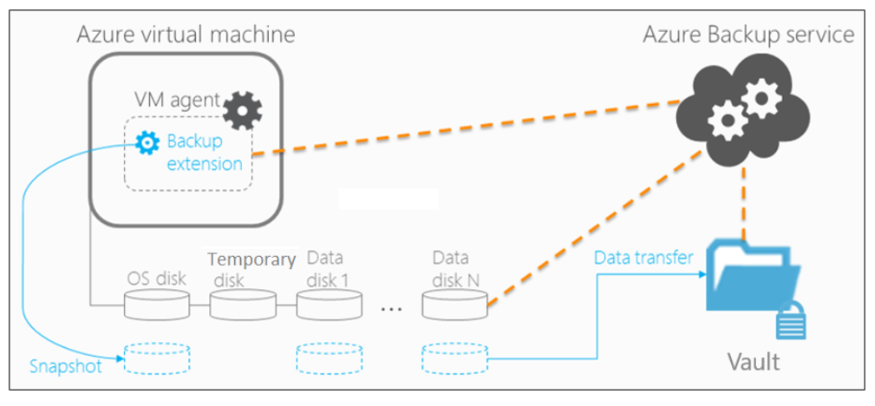
Azure Backup performs the following steps:
- Backup job runs based on the defined schedule.
- If the VM is active:
- Backup extension is installed (VM Snapshot or VM SnapshotLinux).
- Snapshot is taken and stored locally.
- Data is transferred to the vault in parallel per disk.
- Only changed data blocks (delta) are sent.
- Snapshot transfer to the vault may take several hours, but daily backup completes within 24 hours.
Additional Security
- Vault Encryption: Enable vault encryption with Customer-Managed Keys (CMK).
- Enhanced Soft Delete: Protects backups from accidental deletion or malware, even with “always-on” option.
Azure Backup provides an automated, secure, and cost-effective VM backup solution with no additional infrastructure needed.
Restoring Data on a VM
Organizations with a Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BCDR) plan typically schedule drills to ensure the business can recover from disasters.
Types of Recovery
Azure Backup provides several ways to restore VMs. Users can perform instant recovery from the snapshot tier (ideal for operational recovery) or from the vault tier.
| Recovery Option | Details |
|---|---|
| Create new VM | Quickly create and run a new VM from the restore point. The new VM must be created in the same region as the source VM. |
| Restore disk | Recover VM disks to be used to create a new VM. Disks are copied to a specified resource group. Azure Backup provides templates to help create the VM. Users may also attach the disk to an existing VM. |
| Replace existing | Restore disks to replace those on an existing VM. Azure Backup takes a snapshot before replacement and stores it in a specified staging location. Not available if the VM has been deleted. |
| Cross-region restore (secondary region) | Restore the VM in a secondary (Azure paired) region. Supports “Create VM” and “Restore Disk” options, but not “Replace existing”. |
| Cross-subscription restore | Allows restoring the VM or disk to a different subscription within the same tenant. Enabled via properties in the Recovery Services Vault. Supported for VMs with Managed System Identities (MSI). Not supported for snapshot-tier restore points, unmanaged VMs, or encrypted VMs using Advanced Digital Encryption (ADE). |
| Cross-zonal restore | Restore VM or disk to a different Azure zone. Supported only for managed VMs with Zonal Redundant Storage (ZRS) enabled. Not applicable to snapshot-tier restore points or encrypted VMs. |
| Selective Disk Backup | Enables partial VM disk backup and recovery via Enhanced Policy. Users can back up and restore a subset of critical disks from snapshot or vault tier. |
File Recovery from Backup
Users can restore individual files from a recovery point by mounting the snapshot to a target machine using an iSCSI initiator.
Learn more in the docs: Restore files from an Azure VM backup
Recovering Encrypted Virtual Machines
Azure Backup supports backup and recovery of VMs encrypted using Azure Disk Encryption. This encryption works with Azure Key Vault to manage associated secrets.
Limitations for Encrypted VMs:
- Only supports standalone key encryption. Certificate-based keys not yet supported.
- File/folder-level recovery is not supported. Users must restore the entire VM and manually copy files.
- The Replace existing option is not available for encrypted VMs.
By understanding these options, users can tailor their VM recovery strategy to fit business needs and disaster scenarios.