Introduction to Azure Backup
Azure Backup
IT professionals understand how critical data is to an organization. The need to protect this data drives decisions around storage, backup, and security. Many companies enforce policies specifying backup frequency, retention duration, and recovery procedures.
On-Premises Backup Solutions
For on-premises scenarios, backup solutions may include:
- Local redundant storage
- Off-site storage
- Tape drive backups stored off-site
However, solutions like tape drive backup can delay the recovery process, as the physical tape must be returned to the server room for restoration. This often results in significant downtime.
Challenges with Traditional Backup Solutions
Traditional backup solutions may fail to address key concerns such as:
- Backup security
- Ransomware threats
- Human error during backup/restore
An ideal solution must be:
- Cost-effective
- Easy to use
- Secure
This is where Azure Backup excels.
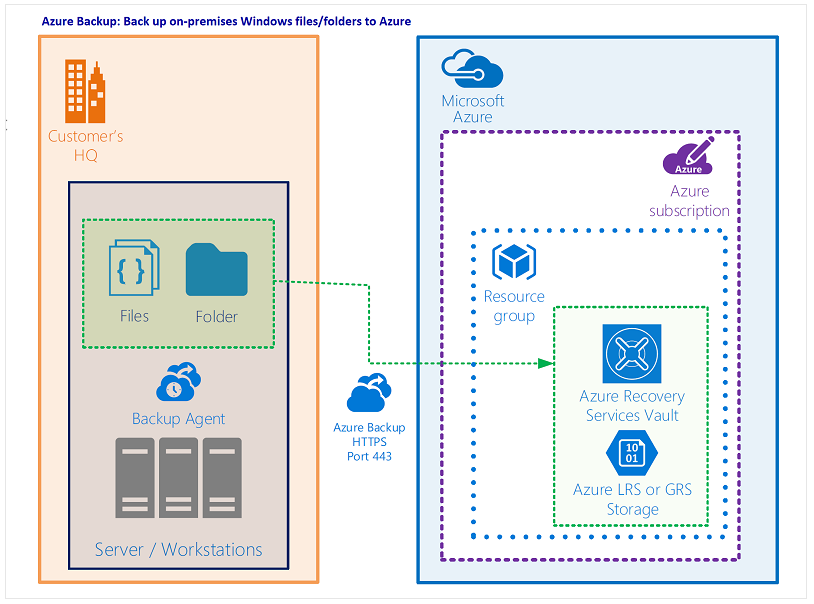
Example Scenario
A user runs an application with a SQL Server database using an Always-On Availability Group across three Azure VMs. The user wants to back up the database using Azure's native backup services.
Goals:
- Retain backups for 10 years in low-cost storage for audit and compliance
- Monitor daily backup jobs across all databases
What is Azure Backup
Azure Backup is a simple, secure, and cost-effective data backup and recovery service from Microsoft Azure.
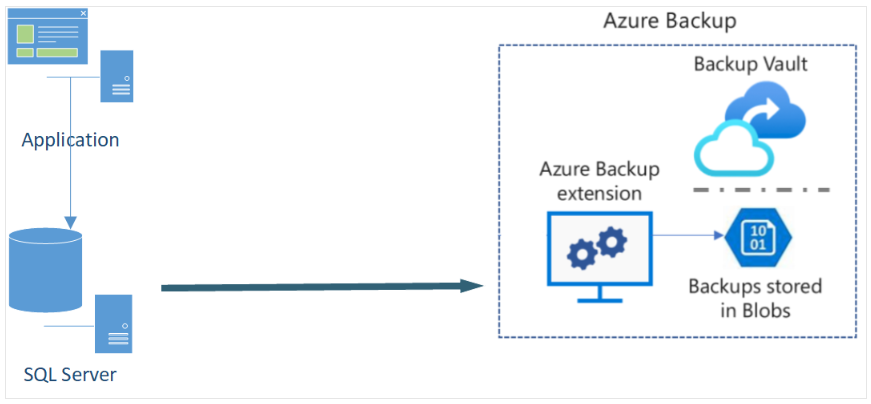
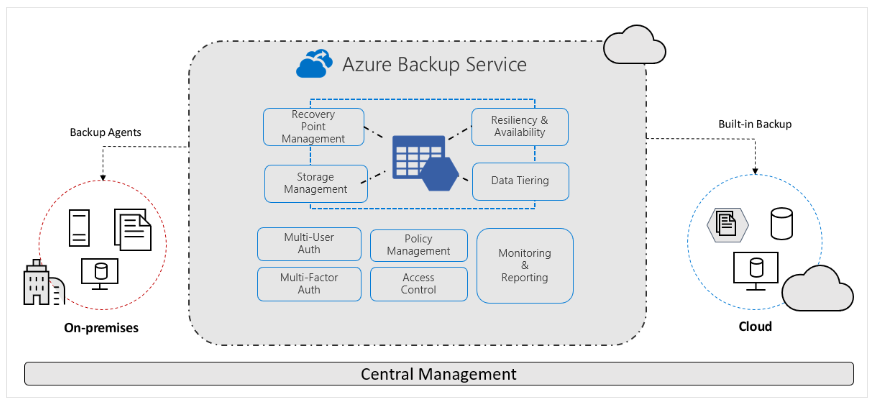 Diagram showing Azure Backup service implementing a backup agent from an on-premises environment to the cloud. The center shows secure and scalable Azure Backup components, with centralized management below.
Diagram showing Azure Backup service implementing a backup agent from an on-premises environment to the cloud. The center shows secure and scalable Azure Backup components, with centralized management below.
Definition of Azure Backup
Azure Backup is an Azure service that provides infrastructure-free, secure, and cost-efficient backup solutions for all Azure-managed data assets.
The centralized management interface allows users to create backup policies and protect various enterprise workloads, including Azure Virtual Machines, Azure Disks, SQL and SAP databases, Azure file shares, and Azure Blobs.
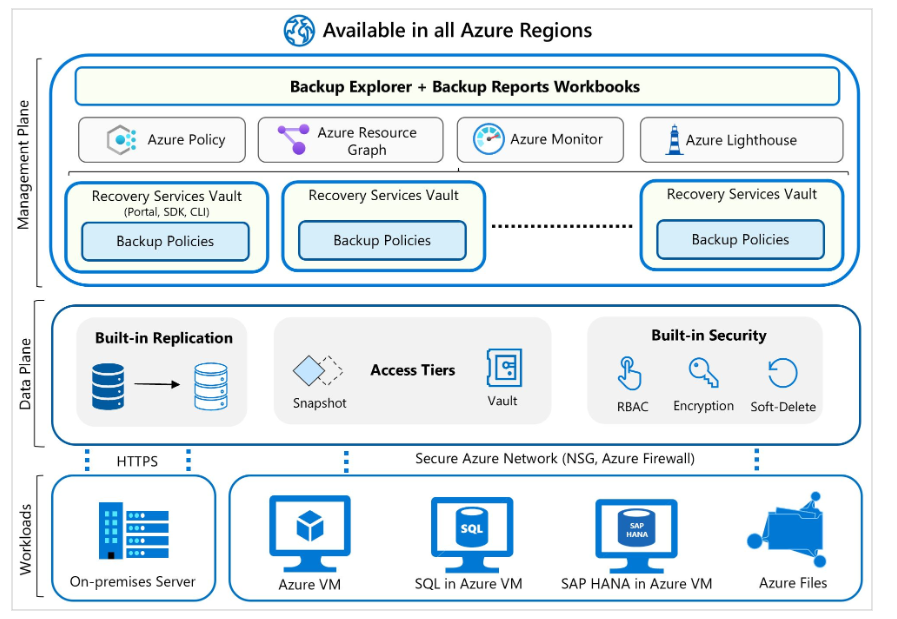 Architecture diagram showing workloads at the bottom, leading to the data plane, and connecting to the management plane, which includes backup policy, Azure Policy, Azure Monitor, and Azure Lighthouse.
Architecture diagram showing workloads at the bottom, leading to the data plane, and connecting to the management plane, which includes backup policy, Azure Policy, Azure Monitor, and Azure Lighthouse.
Azure Backup supports backup services for:
- On-premises files, folders, and OS
- Azure Virtual Machines (VMs)
- Azure Managed Disks
- Azure File Shares
- SQL Server in Azure VMs
- SAP HANA databases in Azure VMs
- Azure Database for PostgreSQL servers
- Azure Blobs
- Azure Database for PostgreSQL – Flexible Servers
- Azure Database for MySQL – Flexible Servers
- Azure Kubernetes Cluster
Key Features
Here are some key features of Azure Backup:
| Feature | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure-free | No need for dedicated backup servers or infrastructure. Azure Backup automatically manages and scales storage. | Reduce capital and operational costs, simplify use with storage automation. |
| Large-scale management | Manage all backups centrally via Backup Center. Use APIs, PowerShell, and Azure CLI for automation. | Simplifies large-scale data protection management and boosts operational efficiency. |
| Security | Azure Backup provides built-in security for data in transit and at rest, including encryption, private endpoints, and alerts. | Protect backups from ransomware, rogue admins, and accidental deletion. |
How Do RTO and RPO Work?
Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is the maximum acceptable time to restore a business process after a disaster.
Example: If a critical app fails and 4 hours of downtime is tolerable, then the RTO is 4 hours.
Recovery Point Objective (RPO) is the maximum acceptable amount of data loss measured in time.
Example RTO and RPO Scenario
A company has an RPO of 1 hour for its customer database, meaning it backs up data every hour. In the event of a loss, a maximum of 1 hour of data would be lost.
If the RTO is set to 3 hours, then access to the database must be restored within 3 hours to minimize operational impact.
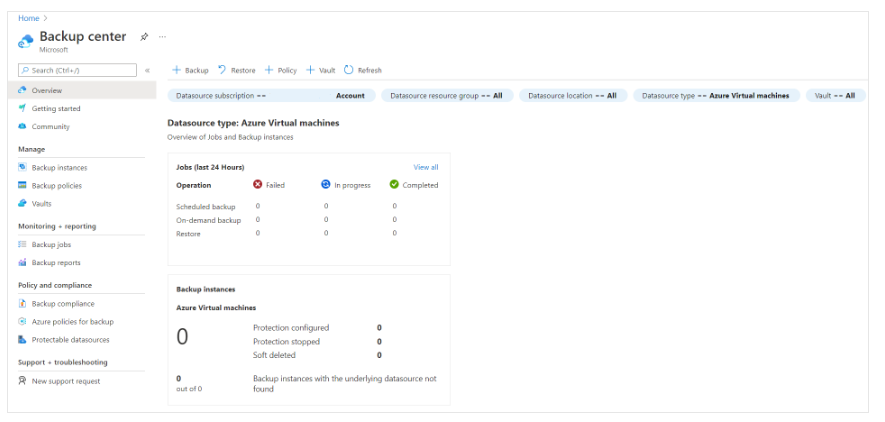
How Azure Backup Works
Let’s examine how Azure Backup works to protect your data. We'll cover how it simplifies backup across different data types and ensures backup security.
Covered in this unit:
- Workload Integration Layer – Backup Extension: Integration with actual workloads like VMs or Azure Blobs.
- Data Plane – Access Tiers: Backup storage has three tiers:
- Snapshot tier
- Standard tier
- Archive tier
- Data Plane – Availability and Security: Data is replicated across zones or regions based on selected redundancy.
- Management Plane – Recovery Services Vault/Backup Vault and Backup Center
What Gets Backed Up and How?
Azure Backup backs up data, machine state, and workloads running on on-premises machines or VM instances to Azure. Backed-up data is stored in a Recovery Services Vault or Backup Vault.
On-Premises
- Windows machines can back up directly to Azure using the Microsoft Azure Recovery Services (MARS) agent.
- Alternatively, backup can be done to a server (e.g., System Center DPM or Microsoft Azure Backup Server (MABS)) and then to Azure Vault.
Azure VMs��
- Azure VMs can be backed up directly.
- Azure Backup installs a backup extension to the VM agent for full VM backups.
- For file/folder backups only, use the MARS agent.
Vault and Supported Backup Types
Vault is an online Azure storage entity for backup copies, recovery points, and backup policies.
Backup Types:
| Type | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Full | Complete database backup including all data and logs. | Once daily or weekly. |
| Differential | Backs up only data changed since the last full backup. | Once daily; cannot run alongside full backups. |
| Multiple per day | Periodic VM backups (min RPO 4h, max 24h). | Use Enhanced Backup Policy. |
| Selective Disk Backup | Backs up only selected disks in a VM. | Save costs by backing up only critical disks. |
| Transaction Log | Backs up transaction logs for point-in-time restore. | Every 15 minutes max. |
Workload Integration Layer – Backup Extension
The backup extension is installed on the source VM or worker VM. During backup, it generates backups via:
- Storage: Snapshots for Azure VMs/files.
- Stream Backup: For SQL/HANA databases.
Data is then securely transferred via NSG, firewall, or private endpoints to Azure Backup storage.
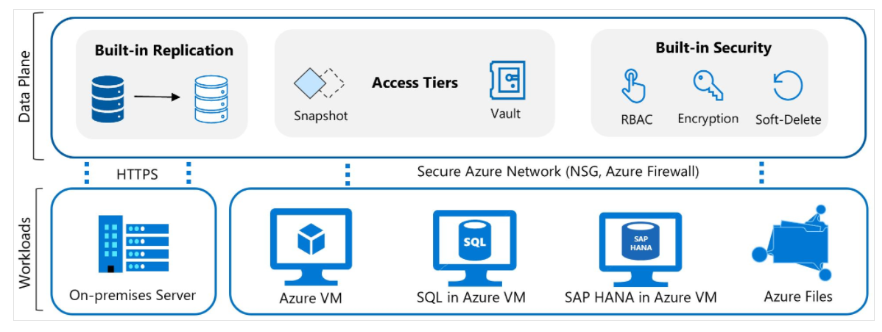
Data Plane – Access Tiers
Three backup storage tiers:
1. Snapshot Tier
- VM snapshots are stored alongside disks.
- Fast restoration as snapshots are local in the resource group.
2. Vault-Standard Tier
- Backup data stored in Azure-managed vaults.
- Isolated secure copies remain even if original data is lost.
3. Archive Tier
- Long-term storage for compliance.
- Rarely accessed old backups stored for archival.
Each tier has different RTO and pricing.
Data Plane – Availability and Security
Backup replication options:
- LRS: Locally Redundant Storage
- GRS: Geo-Redundant Storage
- ZRS: Zone-Redundant Storage
Security:
- Data encryption (at rest and in transit)
- Azure RBAC – restrict who can perform backup/restore
- Soft-delete: Deleted backups are retained for 14 days free of charge
Azure Backup also supports lifecycle management for retention policies.

Management Plane – Vault & Backup Center
Azure Backup uses:
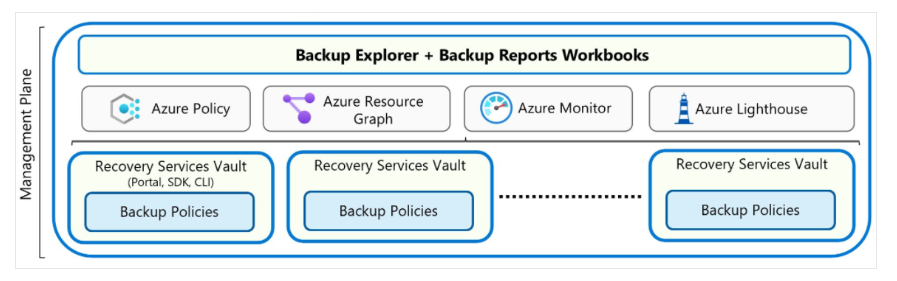
- Recovery Services Vault and Backup Vault to organize and store backup data
- Backup Policies to define schedules and retention durations
- Backup Center to manage backups at scale
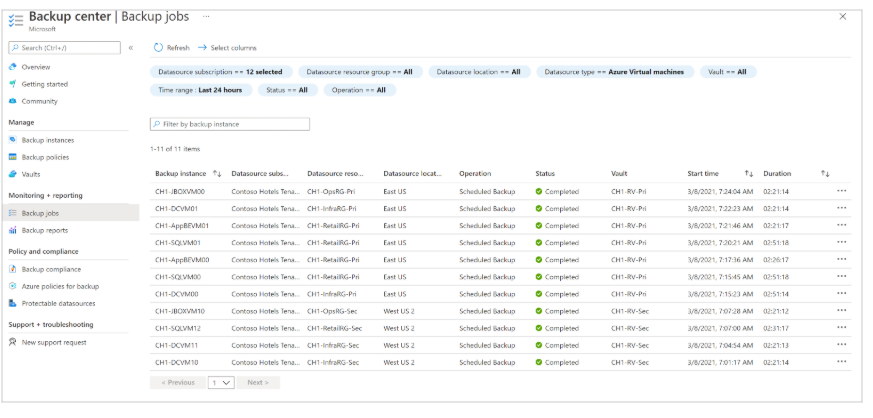
Backup Center
- Single interface to manage all backup jobs
- Designed for large, distributed Azure environments
- Supports cross-workload, vault, subscription, region, and Azure Lighthouse tenant scenarios
When to Use Azure Backup
This section explains when Azure Backup is the right choice for data protection needs. Common backup scenarios where Azure Backup is beneficial include:
- Ensuring data availability
- Protecting Azure workloads
- Securing data
Decision Criteria
Azure Backup is an infrastructure-free and secure backup solution for all Azure-managed assets, including VMs, Disks, SQL and SAP databases, file shares, and blobs.
Key criteria for evaluating Azure Backup:
| Criteria | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Azure Workloads | Azure VMs, Disks, SQL Server or SAP HANA in Azure VMs, Azure Blobs, PostgreSQL databases |
| Compliance | Customer-defined backup policies with long-term retention across zones/regions |
| Operational Recovery | Self-service backup/restore for accidental deletions or data corruption |
Applying the Criteria
Example: An organization runs a SQL Server database across three Azure VMs. Data must be retained for 10 years for compliance. The user wants to monitor backups.
If the three Azure VMs are deployed across different subscriptions or regions, be aware that Azure Backup does not support cross-region backup for most workloads. However, it does support cross-region recovery in paired secondary regions.
Can Azure Backup protect Azure VMs running SQL Server?
Yes. Azure Backup can back up the entire Windows or Linux VM using a backup extension. Users can:
- Back up the entire VM, or
- Use the MARS agent to back up only files, folders, and system state
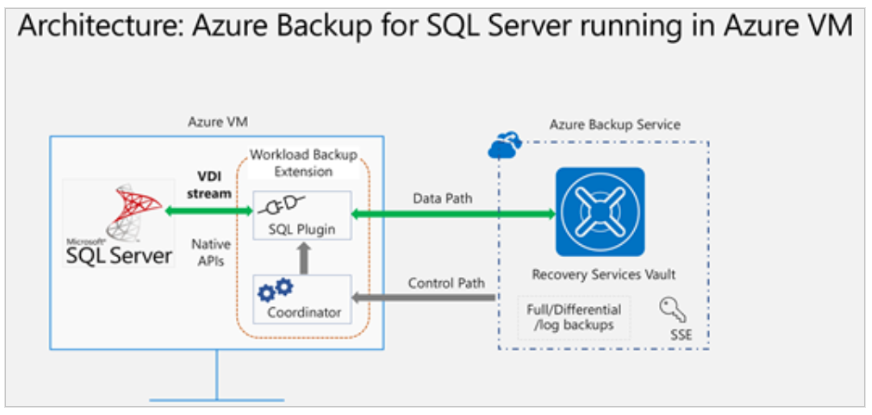
To back up SQL Server data only:
- Azure Backup offers a stream-based solution for SQL Server in Azure VMs that includes:
- Full, differential, and log backups
- 15-minute RPO with frequent log backups
- Point-in-time recovery
- Per-database backup/restore
Does Azure Backup support compliance?
Yes. Users can configure access control for backups. Vaults (Recovery Services or Backup Vault):
- Support management via Azure Portal, Backup Center, vault dashboards, SDK, CLI, and REST API
- Act as RBAC control boundaries – only authorized backup admins can access
Retention:
- Short-term: minutes or daily
- Long-term: weekly, monthly, or yearly
Two Long-Term Retention Types:
- Planned: Data is known to need multi-year retention (e.g., for legal compliance)
- Unplanned: On-demand backups with custom retention settings (not governed by scheduled backup policies)
On-Demand Backup:
- Useful when backup isn't aligned with a schedule
- Suitable for granular backups (e.g., multiple IaaS VM backups per day)
- Retention of these backups does not follow the scheduled policy
Azure Backup Policies allow you to configure backup times and retention durations, and they can be applied across multiple items.
Does Azure Backup Simplify Monitoring and Administration?
Yes. For monitoring and reporting, Azure Backup integrates with Log Analytics and uses Workbooks for reporting.
Monitoring Capabilities:
- Built-in job monitoring for configuration, backup, restore, deletion, etc.
- Suitable for single-vault scale – ideal for small environments
Large-Scale Monitoring:
Use Backup Explorer:
- Aggregated view of the entire backup estate
- Built-in Azure Monitor Workbooks
- Provides detailed insights across:
- Tenants
- Locations
- Subscriptions
- Resource groups
- Vaults