Definition of Cloud Computing
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing is the delivery of computing services over the internet. These services typically include IT infrastructure such as virtual machines, storage, databases, and networking. Cloud services also extend IT infrastructure implementations to cover areas like the Internet of Things (IoT), Machine Learning (ML), and Artificial Intelligence (AI).
In Cloud Computing, there is a concept known as the Shared Responsibility Model, which divides cloud services into types based on the responsibilities shared between the customer and the cloud service provider.
The following diagram illustrates how the Shared Responsibility Model determines who is responsible for what, depending on the type of cloud service used.
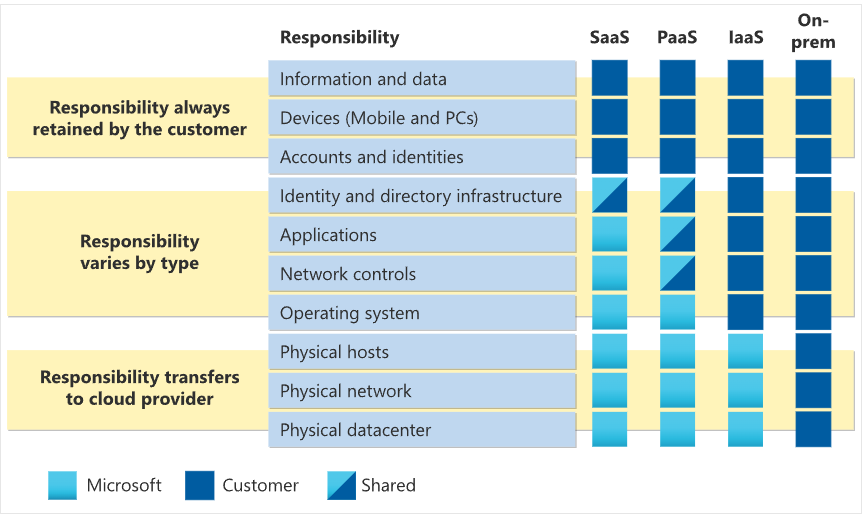
When using a cloud provider, users are always responsible for:
- Information and data stored in the cloud
- Devices allowed to connect to the cloud (phones, computers, etc.)
- Accounts and identities of people, services, and devices in the organization
Cloud providers are always responsible for:
- Data Centers
- Physical Network
- Physical Hosts (Power, Safety, CCTV, Security, etc.)
The selected service model determines responsibility for aspects such as:
- Operating system
- Network controls
- Applications
- Identity and infrastructure
Cloud Computing Models
Cloud models define how cloud resources are deployed. The three main cloud models are private cloud, public cloud, and hybrid cloud.
Private Cloud
A private cloud delivers IT services over the internet but is managed by a single entity or organization. It gives a company and its IT department broad control. A private cloud can be hosted in an on-premises data center or in a third-party data center dedicated solely to that company.
Public Cloud
A public cloud is built, controlled, and maintained by a third-party cloud provider. In this model, anyone can purchase and use the available cloud services.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud combines both private and public clouds into a single, connected environment. This model enhances security, for instance, by designating which services remain on the public cloud and which should run on a private cloud infrastructure.
The following table compares key aspects of each cloud model.

Multi-cloud
A multi-cloud setup uses more than one public cloud provider. This approach is increasingly common for reasons such as:
- Leveraging different features from various cloud providers
- Starting with one provider and migrating to another
- Enhancing resilience and avoiding vendor lock-in
In a multi-cloud environment, users must manage resources and security across multiple cloud providers simultaneously.
Azure Arc
Azure Arc is a tool that helps manage various cloud environments, including:
- Public cloud using Azure only
- Private cloud in your own data center
- Hybrid cloud combining private and public clouds
- Multi-cloud using multiple providers at once
Azure Arc offers greater control and easier management across these cloud scenarios.
Azure VMware Solution
Azure VMware Solution allows users to run VMware workloads in Azure with seamless integration and high scalability. It supports organizations transitioning to the cloud without needing to change existing architecture or infrastructure.
Consumption-Based Model
IT Infrastructure Model Comparison: CapEx vs. OpEx
When comparing IT infrastructure models, there are two types of expenditure to consider:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): One-time upfront spending to purchase or secure physical resources
- Operational Expenditure (OpEx): Ongoing costs for services or products over a period of time
Cloud Computing and OpEx
Cloud computing falls under OpEx because it uses a consumption-based (pay-as-you-go) model. With cloud computing, users don’t need to pay for:
- Physical infrastructure
- Electricity
- Security
- Data center maintenance
Benefits of the Consumption-Based Model in Cloud Computing
- No upfront costs
- No need to purchase and maintain expensive infrastructure that might not be fully used
- Ability to scale up services/resources as needed
- Ability to stop paying for services/resources no longer in use
Cloud Pricing Model Comparison
Cloud computing uses a pay-as-you-go pricing model, meaning users only pay for the cloud services they consume. This helps with:
- Planning and managing operational costs
- Operating infrastructure more efficiently
- Scaling resources in line with business needs